Captive screws are fasteners designed to stay attached to components even when unfastened. They come in various designs, each offering unique functionalities tailored to specific uses. We will provide a guide to the different captive screw designs and installation techniques to help you pick the right one to ensure proper placement and avoid delays, loose screws, or damage.
Fivetech is your best partner for high-quality, ISO-certified, and RoHS-compliant captive screws. Our user-friendly designs, including tool-less options, are trusted by engineers in over 30 countries. From upgrading servers and data centers to developing applications in electric vehicles, smart manufacturing, low-orbit satellites, and robotics, Fivetech delivers reliable, innovative solutions tailored to your needs. Visit Captive Screw/Fastener – Fivetech for our catalog or contact us for customized solutions.
Fivetech’s Key Features:
- Tool-less Operation: Screw/unscrew by hand, boosting efficiency and convenience, especially in confined spaces that are usually hard to reach with bulky tools.
- High-Quality Materials: Utilize durable, corrosion-resistant metals for optimal performance.
- Insulation: Captive thumb screw knobs made out of fire-retardant, heat-resistant plastic to prevent scalding and electrical hazards.
- Customization: Customized options are available with various knob shapes, colors, and assembly methods for a wide range of applications; they also support installation on PCB boards in SMT form.
- Sustainability: Certified by ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management (EMS) and RoHS2 with environmental-focus captive screw designs.
| Picture | Product | Material | Head diameter | Thread | Outer Panel Dimensions | Screw Projection | Knob Height | ||||
| A Min | A Max | T | P-1 | P-2 | H1 | H2 | |||||

|
Fastener Screw |
|
∅8mm | M3*0.5 | 0.8 | ~ | 12 | 0.4 | 4.0 | 11.6 | 8.0 |

|
13 Series Captive Screw |
|
Ø8.5mm | M3*0.5 | 0.8 | ~ | 13.8 | 3.45 | 6.1 | 10.35 | 7.70 |

|
32 Series Captive screw |
|
∅11.5mm | 6-32 | 0.8 | ~ | x | 0.4 | 5.1 | 16.1 | 11.4 |

|
33 Series Captive screw |
|
∅10.6mm | M3-M6 | Customizable specifications. Contact us for details. | ||||||
| ∅10.6mm | 4-40
10-32 |
||||||||||

|
34 Series Captive screw |
|
Ø18mm | M3/#6-32 | 0.8 | ~ | x | 1.3/3.3 | 5.8/7.8 | 16.7 | 12.2 |
|
41 Series Fastener Screw (Mini knob) |
|
Ø6.5mm | M3*0.5 | 1.0 | ~ | 11.6 | 0.6 | 3.8 | 11 | 7.8 |

|
41 Series Fastener Screw (Slot) |
|
Ø8.5mm | M3 | 0.95 | ~ | 15.8 | 0.7 | 7.6 | 15.1 | 8.2 |
| 41 Series Fastener Screw (6L/Slot) | ∅10mm | M3 | 0.8 | ~ | 10.5 | 0.2 | 4.3 | 10.3 | 6.2 | ||
| 41 Series Fastener Screw (Slot) | Ø12mm | M4/#8-32 | 1.4 | ~ | 15.8 | 0.4 | 7.2 | 15.4 | 8.6 | ||

|
43 Series Captive screw |
|
Ø11.5mm | #6-32 | 0.8 | ~ | 10.8
|
0.6 | 4.3 | 10.2 | 6.5 |
| Ø11.5mm | #6-32 | 0.8 | ~ | 12.8 | 1.4 | 5.1 | 10.2 | 6.5 | |||

|
44 Series Fastener Screw |
|
∅6.0mm
|
M2.5 | 0.8 | ~ | 12.6 | 0.6 | 4.3 | 12.0 | 8.3 |
| ∅6.8mm | M3 | 0.8 | ~ | 13.7 | 0.5 | 4.1 | 13.2 | 9.6 | |||
| ∅7.5mm | #6-32 | 0.8 | ~ | 13.7 | 0.5 | 4.1 | 13.2 | 9.6 | |||

|
44 Series Fastener Screw (Hex) |
|
∅6.5mm | M3 | 0.8 | ~ | 16.5 | 2.5 | 6.9 | 14.0 | 9.6 |
| Picture | Product | Material | Head diameter | Thread | Outer Panel Dimensions | Screw Projection | Knob Height | ||||
| A Min | A Max | T | P-1 | P-2 | H1 | H2 | |||||

|
Fastener Screw – |
|
Ø7mm | M3*0.5 | 0.8 | ~ | 15.4 | 0.6 | 4.7 | 14.8 | 10.7 |
|
Captive Screw- |
|
∅11mm | M3*0.5 | 1.0 | ~ | 15.6 | 0.3 | 4.6 | 15.3 | 11.0 |

|
Captive Screw- |
|
∅11mm | M3*0.5 | 0.8 | ~ | 15.9 | 0.7 | 6.1 | 15.2 | 9.8 |

|
Captive Screw- |
|
∅11mm | M3*0.5 | 0.8 | ~ | 12.6 | ~ | 3.6 | 12.7 | 9.0 |

|
27 Series Captive Screw |
|
Ø 9.5mm | M3*0.5 | 0.8 | ~ | 14.6 | 0.2 | 4.2 | 14.4 | 10.4 |

|
27 Series Captive Screw-press in |
|
Ø10mm | M3 | 0.8 | ~ | 15.6 | 0.5 | 4.4 | 15.1 | 11.2 |
| 27 Series Captive Screw-flare in | Ø10mm | M3 | 1.0 | ~ | 15.6 | 0.6 | 4.2 | 15.2 | 11.4 | ||

|
27 Series – Smooth Knob-Press in |
|
Ø10mm | M3 | 0.8 | ~ | 15.6 | 0.5 | 4.4 | 15.1 | 11.2 |
| 27 Series – Smooth Knob-Flare in | Ø10mm | M3 | 1.0 | ~ | 15.6 | 0.6 | 4.2 | 15.2 | 11.4 | ||

|
27 Series Captive Screw-press in |
|
∅11.5mm | 6-32 | 0.8 | ~ | X | 0.6 | 5.8 | 15.9 | 10.7 |
| 27 Series Captive Screw-PC board type | ∅11.5mm | 6-32 | 1.6 | ~ | X | 1.3 | 6.5 | 15.2 | 10.0 | ||

|
27 Series Captive Screw-Floating |
|
Ø13mm | M5 | 0.8 | ~ | 21.2 | 5.0 | 10 | 16.2 | 11.2 |

|
27 Series – High Profile |
|
Ø13.35mm | M5*0.8 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 31.5 | 1.7 | 13.5 | 29.8 | 18 |

|
27 Series – High Profile |
|
∅14.7mm | M6*1.0 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 31.0 | 3.4 | 13.7 | 27.6 | 17.3 |

|
27 Series Captive Screw- Floating |
|
Ø18mm | M3*0.5 | 0.8 | ~ | 14.6 | 0.2 | 4.2 | 14.4 | 10.4 |

|
27 Series Captive Screw- Flare in |
|
Ø18mm | M5/ #10-32 |
1.0 | ~ | 21.2 | 1.3 | 6.05 | 19.9 | 15.15 |

|
27 Series Captive Screw- Press in |
|
Ø18mm | M5/ #10-32 |
1.0 | ~ | 21.2 | 0.7 | 5.4 | 20.5 | 15.8 |
Searching for a suitable solution for your design?
1.What is a Captive Screw?
A captive screw is a fastener designed to remain attached to a component, even when it is unfastened. This prevents the loss of screws during disassembly or maintenance, which is vital to maintain efficiency and safety in various industries, such as machinery, electronics, furniture, and automotive.
1.1. Captive Screw Components
A captive screw assembly comprises several key components that work together to provide a secure and reliable fastening solution:
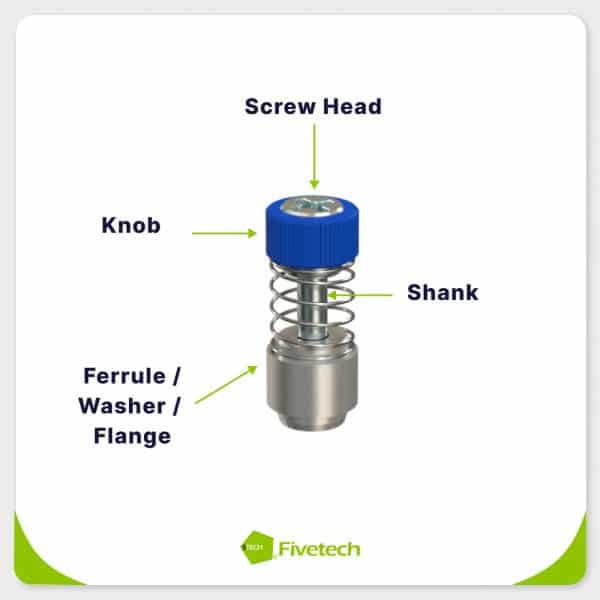

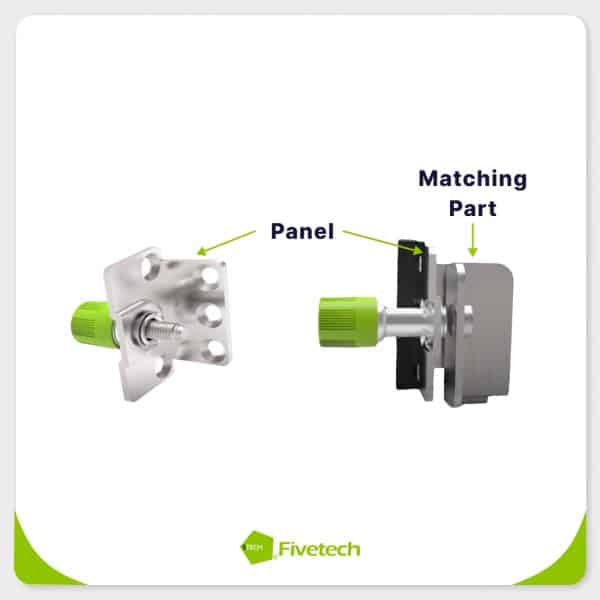
- Matching Part: This is the primary structure which the captive screw and panel are attached to. It houses a threaded hole that accommodates the screw’s shank.
- Panel: The panel is the component secured to the matching part using the captive screw. It can be made from various materials such as metal, plastic, or glass.
- Screw Head: The top of the screw has a drive that allows for tightening or loosening using specific tools. Common drive types include Phillips, slotted, hex, Torx, etc.
- Knob: Fivetech captive screws feature a knob design around the screw head, allowing tool-less, manual operation.
- Shank: The rod length of the shank has a reduced diameter and it has a threaded end that can be connected to the matching part.
1.2. How Does It Work?
The shank will first pass through a clearance hole in the panel, then the threaded end will be fastened into the threaded hole in the matching part. When it is unfastened, this threaded portion of the screw will be disconnected from the matching part, while the retaining mechanism prevents the captive screw from detaching off the panel.
Moreover, with the unique and convenient knob design on Fivetech’s captive screw, users can fasten/unfasten screws without the use of tools, so they are no longer limited to the drive on the screw head. With this, the overall process can be simplified to reduce downtime. We also offer a wide range of captive fastener designs with various material options, including stainless steel, aluminum, as well as heat-resistant and fire-retardant plastic. Explore our captive screw catalog to learn more!
Searching for a suitable solution for your design?
2. How to Choose the Best Captive Screw
Not only should you decide on captive screws based on costs and budget, but you must also consider the following factors to ensure optimal performance for your specific applications:
- Load-bearing Capacity: This is influenced by screw diameter, thread pitch, and material. A larger diameter and coarser pitch generally provide greater strength, while each material has varying properties, so be sure to choose one that is strong enough to withstand the anticipated loads.
- Panel Thickness: To ensure adequate engagement and secure fastening, you must ensure the screw length exceeds the panel.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature, humidity, chemical exposure, vibration, and shock can significantly impact screw performance, so make sure to select materials and coatings that are resistant to these factors.
- Safety Features: For applications that involve higher risks of electrical shocks, scalding, or damage, safety features like insulating plastic materials or security mechanisms may be necessary.
- Aesthetics: It is also ideal to choose a captive screw that complements the overall design of your equipment to maintain an appealing look.
Searching for a suitable solution for your design?
3. An Overview of Captive Screw Installation
The installation method we will discuss below refers to the way the ferrule is installed and held ‘captive’ to the panel. Primarily, there are four installation methods: press-in, flare-in, floating, and surface mount technology (SMT). Each method has a high level of permanence, but they are distinct in terms of sturdiness, ease of installation, and tool requirements. Here is a quick comparison:
| Installation Method | SMT | Press-In | Flare-In | Floating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sturdiness | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Ease of Installation | Easy: Fully automated process, allowing high precision while minimizing the need for manual labor |
Medium: Must be manually installed using a machine press or tool, but doesn’t require special holing equipment. |
Slightly Harder: Requires specific tooling to create a slotted hole for installation, making it more complicated than press-in. | Slightly Harder: Requires specific tooling to create a slotted hole for installation, similar to flare-in. |
| Tools Required | Soldering equipment (solder paste, pick and place machine, reflow oven, etc.) | Machine press or manual pressing tool | Machine press and holing tool | Machine press and holing tool |
We’ll dive deeper into the principles behind these techniques and their common applications in the sections below.
3.1. SMT Captive Screw Installation
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a manufacturing process where electronic components are placed and soldered directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). The entire process is automated with cutting-edge equipment on an assembly line, ensuring precision, consistency, and efficiency in captive screw installation.
This method begins with solder paste printing, where a stencil is used to apply a precise amount of solder paste to the PCB’s designated pad areas. The captive screw ferrule will then be placed onto the prepared pad using automated pick-and-place machinery which integrate a vacuum absorber and infrared positioning technology. Once the screw is placed, the PCB will undergo the reflow soldering process, melting the solder paste to create a robust and permanent bond between the ferrule and the PCB.
Installing captive screws with SMT doesn’t just increase production speed and reduce labor costs with automated equipment, it also provides excellent strength and durability, making it ideal for applications that involve compact designs and require high reliability, including electronic enclosures and automotive modules.
3.2. Press-in Captive Screw Installation
Press-in captive screw installation involves inserting a ferrule into a pre-drilled hole in a panel using mechanical force. The ferrule is designed with a slightly larger diameter than the hole. As the ferrule is pressed into the panel, the surrounding material of the panel is displaced and forced (coldflow) into an undercut within the ferrule, forming a secure lock to prevent it from loosening.
This process is relatively simple and straightforward, allowing users to install captive screws with minimal expertise. It even enables installation of fasteners when users don’t have access to both sides of the panels, since the machine press will only be used on the screw head. By relying on pressure and friction, press-in screws maintain a stable connection over extended use. Furthermore, this method also eliminates the potential drawbacks associated with soldering, such as the risk of thermal damage and weld splatter that can harm nearby components.
In terms of application, this cost-effective method is suited for installing panels on automotive, electronic devices, server cabinets, light-duty machinery which operate under low vibration conditions, etc. However, the ductility and softness of the panel have to be considered as well, because this method is reliant on material displacement. Thus, plastic and PCBs should be avoided as they could be damaged; iron is ideal; aluminum and steel have to be tested to ensure compatibility.
When installing press-in screws, it’s also crucial to consider the size of the hole and the thickness of the panels. If the panel is too thin, it won’t have enough material to provide sufficient friction to hold the components together securely. This can impact the overall performance and stability of the assembled product, potentially causing it to loosen or fall off when subjected to vibration or dynamic loads.
3.3. Flare-In Captive Screw Installation
Flare-in captive screws are installed by creating a conical hole in the panel. Once the ferrule of the screw is inserted through this hole, it will experience pressure and deform, expanding outwards to create a flared lip. This expanded part will grip the interior walls of the panel, securing the captive screw in place to prevent detachment during operation.
Due to the minimal force used for installation and the way it does not impact the panel, flare-in captive screws are well suited for applications on thin panels made from various materials, including any metals, plastics, or composites which are prone to damage when subjected to the larger force required for press-in installation. The flush finish of flare-in screws also contribute to a cleaner and more professional aesthetic. Additionally, compared to press-in screws, the expanded ferrule of the flare-in design provides superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to vibration, making it ideal for demanding applications in industrial equipment and aerospace.
Nevertheless, it is important to note that there are still limitations in terms of panel thickness when it comes to the flare-in method. If the panel is too thin, it might still be damaged during installation and the expanded part of the screw won’t have enough material to grip onto, making it prone to loosening. On the other hand, if the plate is too thick, the screw’s flared lip might not be able to expand fully, resulting in a poor fit and a weaker connection. Thicker panels would also require more force for screw installation, making the process more difficult and potentially damaging.
3.4. Floating Captive Screw Installation
Floating captive screws are affixed to the panel along with a flat ring-shaped washer. The screw ferrule will be first inserted through the hole in the panel and fitted with a washer. And then, a press will be used to flatten the ferrule, causing it to grip the washer and attach to the panel.
The washer allows more space between the floating captive screw and panel, unlike the press-in, flare-in, and SMT screws which are attached directly onto the panels. This design feature enables slight movement for the screw, enhancing the overall flexibility of the screw assembly to absorb tolerances, so it can be widely used in various applications, such as electronic equipment, automobiles, mechanical equipment, and other devices where precise alignment is crucial yet difficult.
Plus, with the washer, the impact on the panel will be minimized greatly during the pressing process, making the floating screw suitable for use with softer materials like aluminum, or applications on PCB components, thanks to the reduced risk of deformation or damage.
Moreover, this installation method reduces friction and wear between the screw and the panel, thereby extending their lifespan to allow long-lasting performance. Compared to other methods, maintenance and repair can also become simpler with floating installation, as the screw can be removed more easily without damaging the surrounding structure.
3.5. Things to Keep in Mind During Captive Screw Installation
Now that we covered the installation methods, here are 3 things you should be aware of to improve the performance of your captive screws and avoid complications:
- Maintain the specified distance between the captive screw and the panel’s edge to prevent damage and ensure proper function.
- Use the recommended installation force to avoid damaging the panel or distorting the fastener head and thread.
- Make sure the captive screw is installed from the appropriate side (from the screw head or under the panel) to optimize load distribution and prevent damage to components.
Searching for a suitable solution for your design?
4. Types of Captive Screw Design
Captive screws come in a variety of designs, each tailored to different applications. This section will explore several key specifications, including the screw’s function, body material, knob design, finishing/coating material, and screw size. By understanding these options, you can make informed decisions to optimize your assembly process.
4.1. Function
Other than the captive mechanism, captive screws often include additional features that enhance their overall functionality. For example, they may incorporate springs, knobs, security sleeves, etc.
Spring-loaded captive screws are designed with a built-in spring that is compressed as the screw body is fastened. Conversely, the spring automatically retracts from the matching part when the screw is unfastened, allowing for easy panel access.
Captive thumb screws are equipped with large knobs which offer convenient hand operation, eliminating the need for tools. This makes them especially convenient for applications that frequent access or maintenance since thumb screws can be quickly installed or removed to save time. Plus, the knobs are typically made out of plastic, so they can provide insulation and dissipate heat to prevent electrical hazards as well as scalding.
Captive security screws incorporate unique security mechanisms, such as special screw heads or sleeves, that require specific tools to unfasten. This prevents unauthorized access, making them ideal for protecting sensitive equipment and data.
Furthermore, there are also captive angle screws that are designed for securing vertically situated components or panels. They provide flexibility in terms of installation angles and directions, which makes them particularly useful in applications where space is limited or unconventional positioning is required.
4.2. Screw Body Material
Captive screw components are usually constructed from multiple materials which offer distinct characteristics for each part. Selecting the appropriate material is crucial to ensure the screw’s performance, durability, and compatibility with the application. Here are some of the common materials for captive screws:
- Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance and durability, stainless steel is a popular choice for applications exposed to harsh environments or where aesthetics are important.
- Carbon Steel: While less corrosion-resistant than stainless steel, carbon steel is highly malleable, strong, and cost-effective, making it one of the most commonly used metals.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum is suitable for applications where weight reduction is a priority. Although it may not be as strong as steel, it still offers a great strength-to-weight ratio, as well as electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Brass: It has good corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. However, brass is more often used in decorative applications because of its attractive color tone and relative softness.
- Bronze: Known for its non-magnetic properties, superior corrosion resistance, and rich appearance, bronze is often used in applications where durability and aesthetics are crucial, particularly in marine environments as they can withstand the corrosion of salt water.
- Titanium: Titanium offers high-strength, lightweight material with excellent corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in aerospace and medical applications due to its durability against high temperatures and chemical exposure.
Fivetech offers a wide range of captive screws made from various composite materials and alloys. This allows the screw to have balanced properties that can be tailored to different applications. For more details on the specific materials available, please visit Fivetech’s Captive Screws and Fasteners catalog.
4.3. Knob Design and Material
As we’ve mentioned earlier, there are captive thumb screws that incorporate a knob feature to enable tool-less operation and boost functionality. These knobs also have various designs that can impact the captive screw’s overall ergonomics and aesthetics, common types include:
- Wing Knob: This is a type of knob that features two protruding wings, allowing for efficient tightening and loosening. This design provides a secure grip and enables operators to apply significant torque for reliable fastening.
- Knurled Knob: Knurled patterns on the knob provide enhanced grip, making it easier to tighten and loosen with your fingers.
- Push-Pull Knob: These versatile knobs require either pushing or pulling to operate. Its operation is straightforward and intuitive, but the smooth, rounded head shape can sometimes make it too slippery to grip.
- Prong Knob: This type of knob has multiple prongs, so it can offer a secure grip, enabling users to turn it and fasten the screw with higher torque.
- T-handle knobs: These knobs have a long, straight handle that provides excellent leverage for tightening and loosening. The design also provides great strength and torque for secure fastening.
These knobs may also be designed with different materials. For instance, metal knobs made from aluminum, stainless steel, brass, or others offer more strength and excellent conductivity, as well as an industrial look. In contrast, plastic knobs made out of nylon, thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), or polypropylene (PP) are lightweight, have high insulative properties, and a comfortable grip. There are also manufacturers, like Fivetech, that create captive screw knobs with heat-resistant and fire-retardant PA9T nylon, which enhances the overall durability and safety of the knob.
4.4. Coating Material
Captive screws are usually finished with zinc or nickel coatings to increase their resilience, oxidation resistance, and overall durability. Consider factors such as the environment the screw will be exposed to, the desired level of corrosion protection, and any aesthetic preferences to choose the optimal coating material for your captive screw. Zinc coatings offer relatively better corrosion resistance, while nickel coatings are ideal for applications that require more hardness and wear resistance.
4.5. Screw Size
You must select the appropriate captive screw size to ensure proper fit and reliable performance in your specific applications. Several factors influence screw size, including thread size, pitch, overall length, thread length, and head diameter.
Thread pitch must be compatible with the mating threads or receptacles in your application to ensure a secure connection and compatibility, while the overall length of the screw should be sufficient for proper engagement and fastening without exceeding available space or interfering with adjacent components. Moreover, the thread length is crucial for providing adequate engagement with the mating component. Furthermore, the head diameter must allow for easy access and tightening while avoiding interference with nearby components due to space constraints.
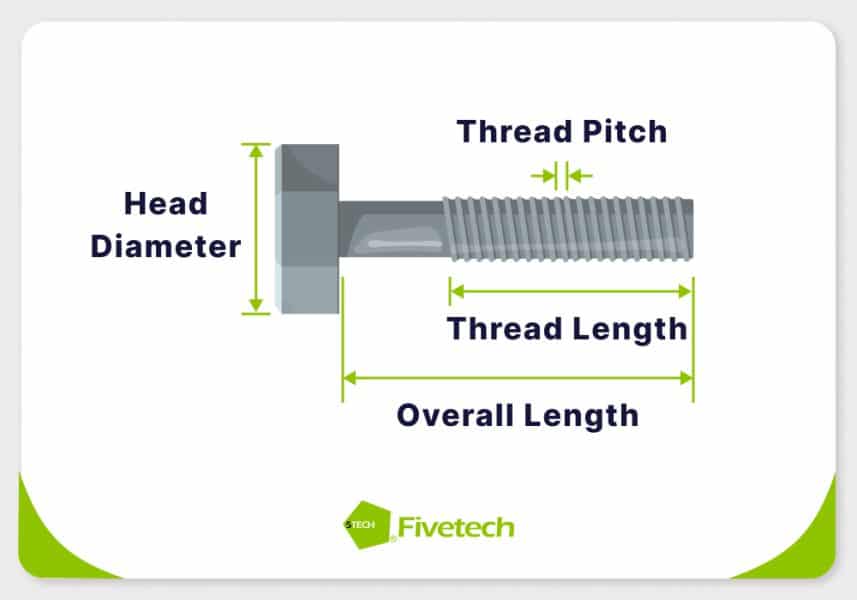
Fivetech offers various captive screw sizes, with a wide option of thread sizes, screw lengths, and head diameters to accommodate different applications and assembly requirements. We also provide customization services to meet specific requirements, ensuring a perfect fit for unique applications.
If you are unsure about your screw size requirements, you can refer to our guide on how to measure screws, bolts, and thread sizes for further details.
5. Explore a Wide Range of Captive Screws Options at Fivetech
Bottom line, captive screws come in various installations and design options that provide reliability as well as convenience in multiple applications. Their ability to remain attached to panels prevents the loss of screws and potential hazards in industrial machinery. With this, captive screws have become essential hardware for many commercial and industrial applications that are often required to meet safety standards.
To explore a wide range of captive screw options which are ISO-certified and RoHS-compliant, including those with user-friendly and tool-less plastic knobs, visit Captive Screw/Fastener – Fivetech, Quarter Turn Fastener, Quick Release Fasteners, M.2 Board Latches, PCB Stanoffs, Folding Handles, Server Hardware Components for our catalog or contact us for customized solutions.
Searching for a suitable solution for your design?